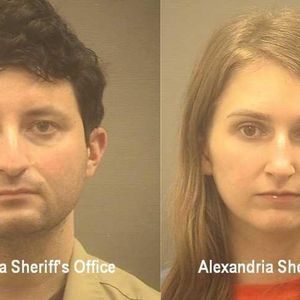
BitcoinWorld Bitfinex Hacker Ilya Lichtenstein Granted Shocking Early Release Under First Step Act In a stunning legal development, Ilya “Dutch” Lichtenstein, the convicted mastermind behind the monumental 2016 Bitfinex hack, has secured early release from federal prison. This surprising turn of events, reported by DL News in early 2025, follows his November 2024 sentencing to five years for orchestrating one of cryptocurrency’s most infamous thefts. Consequently, his release under the U.S. First Step Act raises profound questions about justice, rehabilitation, and the evolving legal landscape for digital asset crimes. Bitfinex Hacker Early Release Details and Legal Mechanism The U.S. Department of Justice confirmed Ilya Lichtenstein’s early release this week. Authorities applied provisions of the First Step Act of 2018. This bipartisan federal law specifically aims to reduce recidivism. Furthermore, it promotes inmate rehabilitation through earned time credits. Lichtenstein reportedly qualified for these credits by participating in prison programming. His original five-year sentence stemmed from a guilty plea to conspiracy to commit money laundering. The charges connected directly to the 2016 Bitfinex security breach. Prosecutors originally charged Lichtenstein and his wife, Heather Morgan, in February 2022. Their arrest followed a multi-year investigation by Homeland Security Investigations (HSI). Agents traced the movement of 119,754 Bitcoin stolen from Bitfinex. At the time of the theft, the cryptocurrency was worth approximately $71 million. However, by the time of their arrest, its value had ballooned to a staggering $4.5 billion. This case remains one of the largest financial seizures in U.S. history. The 2016 Bitfinex Breach and Investigation Timeline Understanding the early release requires examining the original crime’s scale. The Bitfinex hack occurred on August 2, 2016. Attackers exploited a vulnerability in the exchange’s multi-signature wallet service. They successfully initiated over 2,000 unauthorized transactions. These transactions drained customer and corporate funds. The exchange immediately suspended all trading. It also announced a 36% socialized loss across all user accounts. For nearly six years, the stolen funds remained dormant. Then, in 2022, blockchain analytics and traditional investigative work converged. The IRS Criminal Investigation (CI) Cyber Crimes Unit and HSI followed a complex trail. They linked the funds to wallets controlled by Lichtenstein and Morgan. A court-authorized search of their cloud storage accounts revealed private keys. These keys directly accessed the wallets holding the stolen Bitcoin. Key Events in the Bitfinex Case Date Event Aug 2, 2016 Bitfinex hack occurs; 119,754 BTC stolen. Feb 8, 2022 Lichtenstein and Morgan arrested in New York. Aug 2022 Both plead guilty to money laundering conspiracy. Nov 2024 Lichtenstein sentenced to 5 years in prison. Early 2025 Early release granted under First Step Act. The investigation showcased unprecedented collaboration. Agencies combined blockchain forensic tools with classic financial sleuthing. This approach set a new standard for prosecuting cryptocurrency crimes. First Step Act Provisions and Application to Cybercrime The First Step Act represents a significant shift in federal sentencing policy. Its primary goals include: Reducing mandatory minimum sentences for certain non-violent drug offenses. Expanding early release programs through earned time credits. Increasing rehabilitation programming within federal prisons. Improving conditions and reducing recidivism rates. Inmates earn credits by participating in Evidence-Based Recidivism Reduction (EBRR) programs. These programs address needs like vocational training, education, and substance abuse treatment. Lichtenstein’s eligibility suggests he engaged with such programming. The Act does not distinguish between crime types for credit eligibility. Therefore, non-violent financial crimes like money laundering qualify. This application to a high-profile cybercrime case is particularly noteworthy. Impact on Cryptocurrency Security and Legal Precedents Lichtenstein’s early release sends ripples through the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Firstly, it tests the deterrent effect of prosecution for digital asset theft. Secondly, it highlights the tension between punishment and rehabilitation for technical crimes. The case already established several key legal precedents: Asset Forfeiture: The government successfully seized and sold billions in stolen crypto. Jurisdiction: U.S. courts asserted authority over crimes involving globally dispersed digital assets. Investigation Methods: The use of blockchain analytics as evidence gained judicial acceptance. Security experts note the hack forced major exchanges to overhaul their protocols. Today, most leading platforms use sophisticated cold storage solutions. They also employ multi-party computation (MPC) for key management. The Bitfinex incident remains a cautionary tale for the entire industry. Expert Analysis on Sentencing and Release Legal scholars specializing in cyberlaw offer critical perspectives. Professor Elena Carter of Stanford Law School notes, “The First Step Act focuses on rehabilitation for non-violent offenders. The court likely viewed the technical nature of the crime as non-violent, despite its massive financial scale.” Meanwhile, blockchain forensic analyst David Chen observes, “This early release doesn’t diminish the investigative breakthrough. The real victory was tracing and recovering the funds, which returned value to victims.” The case also involved Heather “Razzlekhan” Morgan, a rapper and entrepreneur. She received a shorter sentence and was released earlier. Their combined story of tech savvy, money laundering through complex transactions, and unconventional public personas captured global media attention. Conclusion The early release of Bitfinex hacker Ilya Lichtenstein under the First Step Act concludes a landmark chapter in cryptocurrency legal history. This case demonstrated the formidable reach of U.S. law enforcement into the blockchain. It also tested new sentencing reforms on a high-stakes financial crime. Ultimately, the recovery of $4.5 billion in stolen assets stands as the investigation’s enduring legacy. The industry now watches how this precedent influences future prosecutions of digital asset theft and money laundering. FAQs Q1: What was the First Step Act, and why did it apply to Ilya Lichtenstein? The First Step Act is a 2018 U.S. federal law designed to reform sentencing and promote inmate rehabilitation. It applied to Lichtenstein because he qualified for earned time credits by participating in prison programming aimed at reducing recidivism, and his crime was classified as non-violent. Q2: How much Bitcoin was originally stolen in the 2016 Bitfinex hack? The hackers stole 119,754 Bitcoin from Bitfinex in August 2016. At the time of the theft, this was worth about $71 million. By the time of the arrest in 2022, the value had appreciated to approximately $4.5 billion. Q3: What happened to the stolen Bitcoin after the seizure? The U.S. government successfully seized the vast majority of the stolen Bitcoin. It then sold portions of the cryptocurrency through authorized auctions and market sales. The proceeds are held as recovered assets, with processes in place for potential victim restitution. Q4: How does this early release affect future cryptocurrency crime prosecutions? Legal experts believe the core precedent—successful investigation, seizure, and conviction—remains intact. The early release reflects sentencing policy, not investigative failure. It may, however, influence plea negotiations and sentencing arguments in future digital asset cases. Q5: What role did Ilya Lichtenstein’s wife, Heather Morgan, play in the crime? Heather Morgan pleaded guilty to conspiracy to commit money laundering and defraud the United States. Prosecutors alleged she helped launder the stolen funds through complex transactions, shell companies, and false invoices. She received a sentence shorter than Lichtenstein’s and was released earlier. This post Bitfinex Hacker Ilya Lichtenstein Granted Shocking Early Release Under First Step Act first appeared on BitcoinWorld .